Navigation » List of Schools, Subjects, and Courses » Geog 001 – Physical Geography » Quizzes » Chapter 3 Quiz
With Answers Good news! We are showing you only an excerpt of our suggested answer to this question. Should you need our help in customizing an answer to this question, feel free to send us an email at  or chat with our customer service representative.
or chat with our customer service representative.
Chapter 3 Quiz
Chapter 3 Quiz
1. Gases are ________ of the atmosphere.
unevenly mixed throughout all levels
evenly mixed throughout all levels
evenly mixed in the upper layers
unevenly mixed in the lower layers
evenly mixed in the lower layers
2. A two-part figure showing the natural formation and breakdown of ozone because of ultraviolet energy.
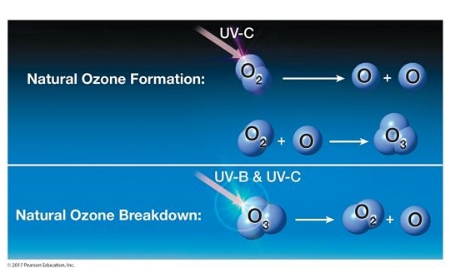
This figure shows the breakdown of ozone in the stratosphere. This breakdown is the result of ________.
a chemical solution
the absorption of ultraviolet energy
CFCs joining with ozone
the reflection of photons
photosynthetic activity
3. The order of the atmospheric layers from the earth’s surface upwards is ________.
thermosphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and troposphere
troposphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, and thermosphere
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere
stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and troposphere
exosphere, stratosphere, troposphere, and mesosphere
4. The ozone layer is in that portion of the atmosphere known as the ________.
heterosphere
mesosphere
stratosphere
troposphere
ionosphere
5. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Oceans and land can store about the same amount of heat per volume.
Oceans and land cool at about the same rate.
Cities near oceans tend to have warmer summers than cities inland.
Land cools more quickly than water.
Oceans cool more quickly than land.
6. Which of the following is NOT considered a pollutant when released by the actions of humans?
Carbon monoxide
Sulfur compounds
Water vapor
Chlorofluorocarbons
Photochemical smog
7. A “hole” in the ozone layer was first discovered over ________.
Antarctica
Africa
the equator
Hollywood
the United States
8. “Weather” and “climate” are ________.
synonyms
differentiated because climate studies the long-term
differentiated because weather is not covered in your textbook
differentiated because climate studies the stratosphere
both atmospheric studies based on many decades of data
9. Which of the following climatic controls can be considered the most important?
Distribution of land and water
Elevation
Longitude
Storms
Latitude
10. The present atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide is approximately 400 ________.
parts per hundred
parts per thousand
parts per billion
parts per trillion
parts per million
11 Which of the following is NOT an atmospheric gas?
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
Water vapor
Clouds
Nitrogen
12. The main impact of ozone on life on the Earth’s surface is to ________.
initiate violent storms
provide oxygen for the atmosphere
act as a lid preventing gases from escaping
reduce ultraviolet solar radiation
serve as a nucleus for cloud formation
13 Which of the following is NOT an important function of Earth’s atmosphere?
Insulates the surface against temperature extremes
Maintains a water supply
Screens out much of the Sun’s ultraviolet radiation
Maintains an envelope of pure oxygen
Supplies the oxygen for life
14. The influence of carbon dioxide on the climate is mainly due to its ability to absorb ________.
infrared radiation
water
ions
helium
argon
15. Which of the following is NOT a “weather element”?
Pressure
Moisture
Latitude
Temperature
Wind
16. The main component of the lower atmosphere by total volume is ________.
helium
water vapor
nitrogen
argon
oxygen
17. The atmospheric layer in which gases do not maintain a uniform composition is the ________.
ionosphere
homosphere
heterosphere
troposphere
stratosphere
18. Ozone is actually ________.
a naturally occurring substance
more healthy to breathe than oxygen
a pollutant caused by the burning of fossil fuels
a form of carbon dioxide
a form of oxygen
19. Photochemical ________ is (are) the result of gases reacting to ultraviolet solar energy in strong sunlight, and forming secondary pollutants.
precipitation
smog
wind
aerosols
erosion
20. ________ is (are) crucial to the formation of clouds in the atmosphere.
Argon
Particulates
Lightning
Neon
Ozone
21. After water vapor, ________ is the most plentiful of the variable gases in the atmosphere.
carbon monoxide
sulfur dioxide
argon
ozone
carbon dioxide
22. Oxygen (O2) is being added to the atmosphere by ________.
vegetation
the burning of coal
animal decomposition
meteorites
solar radiation
23. Mountains act as major climatic barriers with the sheltered or ________ side receiving less moisture than the exposed side.
leeward
north
struck
windward
Coriolis
24. Climatic controls include all but which of the following?
Altitude
Plane of the equator
General circulation of the ocean’s currents
Distribution of land and water
Latitude

