Navigation » List of Schools, Subjects, and Courses » Math 120 – Introductory Probability and Statistics » Quizzes » Quiz 5
No Answers We dont have answer to this question yet. If you need help with your homework send us an email  or chat with our tutors
or chat with our tutors
Quiz 5
Quiz 5
1. A concrete mix is designed to withstand 3000 pounds per square inch (psi) of pressure. The following data represent the strength of nine randomly selected casts (in psi).
3950, 4080, 3300, 3100, 2930, 3820, 4080, 4030, 3470
Compute the mode strength of the concrete. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
- The mode of the strengths of the concrete is ____ psi of pressure. (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.)
- The mode does not exist.
2. Find the population mean or sample mean as indicated.
Population: 2, 8, 10, 16, 24
Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice.

3. The following data represent the monthly cell phone bill for a person’s phone for six randomly selected months.
$35.40, $42.09, $39.47, $38.93, $43.39, $49.26
Compute the median phone bill.
The median phone bill is ______ (Round to the nearest cent as needed.)
4. The following data represent the amount of time (in minutes) a random sample of eight students took to complete the online portion of an exam in a particular statistics course. Compute the mean, median, and mode time.
67.4, 80.6, 88.9, 114.7, 128.4, 102.2, 94.7, 125.7
Compute the mean exam time. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
- The mean exam time is _____ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
- The mean does not exist.
Compute the median exam time. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
- The median exam time is _____ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
- The median does not exist.
Compute the mode exam time. Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice.
- The mode is ____ (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
- The mode does not exist.
5. The following data represent exam scores in a statistics class taught using traditional lecture and a class taught using a “flipped” classroom. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
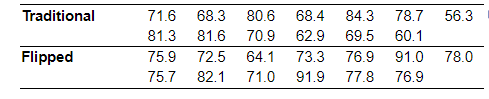
(a) Which course has more dispersion in exam scores using the range as the measure of dispersion?
The traditional course has a range of _____ while the “flipped” course has a range of
The _____ course has more dispersion. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)
(b) Which course has more dispersion in exam scores using the sample standard deviation as the measure of dispersion?
The traditional course has a standard deviation of _____ while the “flipped” course has a standard deviation of ______
The _________ course has more dispersion. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(c) Suppose the score of 60.1 in the traditional course was incorrectly recorded as 601. How does this affect the range?
The range is now _____ (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
How does this affect the standard deviation?
The standard deviation is now ____ (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What property does this illustrate?
- The standard deviation is resistant, but the range is not resistant.
- Neither the range nor the standard deviation is resistant.
- Both the range and the standard deviation are resistant.
- The range is resistant, but the standard deviation is not resistant.
6. A certain standardized test’s math scores have a bell-shaped distribution with a mean of 520 and a standard deviation of 105.
Complete parts (a) through (c).
(a) What percentage of standardized test scores is between 415 and 625? ___ (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(b) What percentage of standardized test scores is less than 415 or greater than 625? ____ (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(c) What percentage of standardized test scores is greater than 730? ____ (Round to one decimal place as needed.)
7. In December 2018, the average price of regular unleaded gasoline excluding taxes in the United States was $3.06 per gallon. Assume that the standard deviation price per gallon is $0.07 per gallon and use Chebyshev’s Inequality to answer the following.
(a) What minimum percentage of gasoline stations had prices within 2 standard deviations of the mean?
(b) What minimum percentage of gasoline stations had prices within 2.5 standard deviations of the mean? What are the gasoline prices that are within 2.5 standard deviations of the mean?
(c) What is the minimum percentage of gasoline stations that had prices between $2.78 and $3.34?
(a) At least ____ of gasoline stations had prices within 2 standard deviations of the mean. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
(b) At least ____ of gasoline stations had prices within 2.5 standard deviations of the mean. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The gasoline prices that are within 2.5 standard deviations of the mean are ______ to _______ (Type integers or decimals. Do not round. Use ascending order.)
(c) _______ is the minimum percentage of gasoline stations that had prices between $2.78 and $3.34.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
8. Which of the following measures of dispersion is resistant, if any? Select all that apply.
- Range
- Standard deviation
- Variance
- None of these measures of dispersion is resistant.
 or chat with our tutors
or chat with our tutors
