Navigation » List of Schools, Subjects, and Courses » Accounting 102 – Managerial Accounting » Quizzes » Quiz 5
With Answers Good news! We are showing you only an excerpt of our suggested answer to this question. Should you need our help in customizing an answer to this question, feel free to send us an email at  or chat with our customer service representative.
or chat with our customer service representative.
Quiz 5
Quiz 5
1.
Which of the following types of companies would typically use process costing rather than job-order costing?
A small appliance repair shop.
A manufacturer of commercial passenger aircraft.
A specialty equipment manufacturer.
A breakfast cereal manufacturer.
2. Conversion cost is composed of _______.
direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead cost
direct material cost and manufacturing overhead cost
all costs included in ending inventory
manufacturing overhead
Knowledge Check Question 02:
Equivalent units is computed using which of the following formulas?
Equivalent units = Number of completed units x Percentage completion
Equivalent units = Number of partially completed units x Percentage completion
Equivalent units = Number of completed units x (100% – Percentage completion)
Equivalent units = Number of partially completed units x (100% ÷ Percentage completion)
3. Which of the following statements about processing costing is false?
Process costing accumulates costs by department.
Process costing assigns departmental costs uniformly to all identical units that pass through the department during a period.
Process costing systems compute unit costs by department.
Process costing is used when a company produces a continuous flow of units that are distinguishable from one another.
4. Clopack Company manufactures one product that goes through one processing department called Mixing. All raw materials are introduced at the start of work in the Mixing Department. The company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Its Work in Process T-account for the Mixing Department for June follows (all forthcoming questions pertain to June):
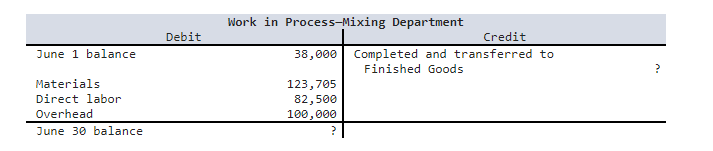
The June 1 work in process inventory consisted of 5,300 units with $20,680 in materials cost and $17,320 in conversion cost. The June 1 work in process inventory was 100% complete with respect to materials and 60% complete with respect to conversion. During June, 37,800 units were started into production. The June 30 work in process inventory consisted of 8,600 units that were 100% complete with respect to materials and 50% complete with respect to conversion.
4. Compute the equivalent units of production for materials.
5. What is the cost of beginning work in process inventory plus the cost added during the period for materials?
6. What is the cost per equivalent unit for materials? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
7. What is the cost of ending work in process inventory for materials? (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 places.)
8 What is the cost of materials transferred to finished goods? (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 places.)
9. Which of the following statements is true?
When materials are purchased in a process costing system, a work in process account is debited with the cost of the materials.
The units in beginning work in process inventory plus the units started into production must equal the units transferred out of the department plus the units in ending work in process inventory.
Statement I is true.
Statement II is true.
Both statements are true.
Neither statement is true.
10. In the cost reconciliation report under the weighted-average method, the “Costs to be accounted for” section contains which of the following items?
Cost of beginning work in process inventory
Cost of ending work in process inventory
Cost of units transferred out
Cost of ending finished goods inventory

