Navigation » List of Schools, Subjects, and Courses » Bio 2450 – Genetics » Final Exam » Final Exam Questions » Final Exam Questions Sample Answers

Question 1
Mendel interpreted his results with garden peas as falsifying ____________
- Cytoplasmic inheritance
- Blending inheritance
- Chromosomal inheritance
- Particulate inheritance
- None of the above
Question 2
In order for a molecule to have all the properties of genetic material it must _______.
- be comprised of RNA
- be comprised of DNA
- Encode information to guide development and cellular function
- Be able to replicate somewhat accurately
- Have the ability to mutate
Question 3
Which description of plants from a true-breeding strain is correct?
- They can reproduce by self-fertilization
- When you ask them a question about breeding they tell it you straight
- They have at least one dominant allele for the trait of interest
- They are homozygous for alleles of the gene(s) that control(s) the trait(s) of interest
- They carry two different alleles for the gene that controls the trait of interest
Question 4
Mendel stated, “ Recessive traits, which are masked in the F1 from a cross between two-breeding strains, reappear in a specific proportion in the F2” He wa providing evidence for his _________.
- Principle of Dominance
- Principle of Uniformity of the F2
- Principle of Segregation
- Principle of Recessivity
- Principle of Independent assortment
Question 5
An organism’s ______ is the genetic makeup of the individual while the ________ is the observable feature of an organism.
- phenotype, genotype
- genophyte, phenotight
- genotype, phenotype
- regulatory sequences, phenotypic appearance
- holotype, allelotype
Question 6
In the F2 -generation in Mendel’s monohybrid cross experiments that ultimately led him to describe “the law of segregation,” the ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes was:
- 3:1
- 1:1
- 1:3
- 9:3:4
- 9:3:3:1
- 2:1
- 12:2:1
Question 7
Mendel (and this course) specifically used a ______________ cross to demonstrate the Law of Independent assortment.
- dihybrid
- Drosophilia
- monohybrid
- unihybrid
Question 8
In pea plants, purple-flowered alleles (P) are dominant to white-flowered alleles (p), while spherical-seed alleles (S) are dominant to wrinkled-seed alleles (s). In an dihybrid cross of two plants that are homozygous for the flower and seed-shape traits, what fraction of the offspring in the F2 should have purple flowers and wrinkled seeds?
- 1/3
- 2/3
- 1/16
- 3/4
- 1/2
- zero
- 9/16
- 1/4
- 3/16
Question 9
Suppose we have one true-breeding strain of tomato that produces red fruit. Suppose we also have a true-breeding strain of tomato that produces yellow fruit. We KNOW that a single gene is responsible for fruit color, and that the red allele is dominant to the yellow allele. You make an F1 cross. What would we expect the appearance of the F2 tomatoes to be?
- 3:1:red:yellow
- 100% red
- 100% yellow
- 3:1:yellow:red
- 50:50:red:yellow
Question 10
Suppose we have a true-breeding strain of pepper plants that produces red fruit. Suppose we also have a true-breeding strain of pepper that produces yellow fruit. We KNOW that a single gene is responsible for fruit color, and that the red allele is dominant to the yellow allele. You make an F2 cross of these two pepper strains and grow them up until they produce ripe fruit: 483 plants produce red fruits, and 103 plants produce yellow fruits. Calculate a X2 value to determine whether the differences you see deviate significantly from Mendelian expectations. A) Do the observed values deviate significantly from the expected? B) What is a potential explanation for this deviation?
- No. The red pepper plants potentially die more often prior to fruiting than the yellow pepper plants.
- Yes. The yellow pepper plants potentially die more often prior to fruiting than the red pepper plants.
- Yes. Sampling error is the most likely explanation for these deviations.
- No. The yellow pepper plants potentially die more often prior to fruiting than the red pepper plants.
- No. Sampling error is the roost likely explanation for these deviations.
- Yes. The red pepper plants potentially die more often prior to fruiting than the yellowpepper plants.
Question 11
An organism’s complete DNA sequence, including all of its coding and noncoding regions is its
- phenotype
- phenome
- genome
- genotype
- pheromone
Question 12
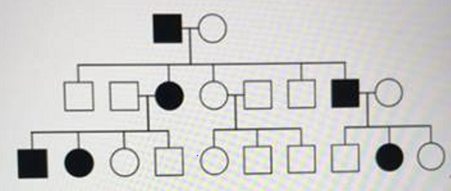
In the above pedigree, what is the mode of inheritance for this trait?
- Y-linked
- Autosomal Recessive
- X-linked recessive
- X-linked dominant
- Autosomal Dominant
- Autosomal Recessive
Question 13.
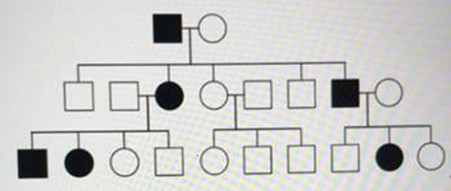
In the above pedigree, ALL of the affected males are?
- Heterozygous
- Hemizygous
- Homozygous dominant
- Homozygous recessive
Question 14
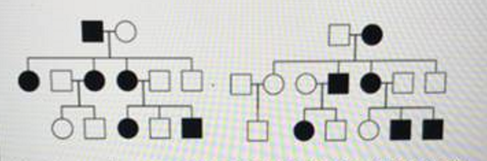
These two pedigrees are most consistent with what form of inheritance?
- X-linked dominant
- Autosomal Dominant
- X-linked recessive
- Autosomal Recessive
- Y-linked
Question 15
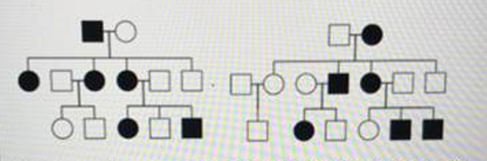
The affected males in this pedigree are:
- homozygous recessive
- heterozygous
- hemizygous
- homozygous dominant
Question 16
In diploid cells of somatic tissue undergoing mitosis, ____________ most certainly carry the same alleles.
- sister chromosomes
- sister chromatids
- homologous chromatids
- homologous chromosomes
Question 18
In Anaphase I of Meiosis, ________are pulled apart to opposite poles
- homologous chromatids
- sister chromatids
- homologous chromosomes
- sister chromosomes
Question 19
Most multicellular animals form gametes through _________.
- Parthenogeesis
- Binary fission
- Sporogenesis
- Mitosis
- Meiosis
Question 20
Most multicellular plants form gametes through ________.
Mitosis
Sporogenesis
Parthenogenesis
Meiosos
Binary Fission
Question 21
In plants haploid spores _________
- divide to form sporophytes
- are gametes.
- undergo meiosis.
- undergo mitosis
Question 22
In humans, the dominance relationship between the A & O alleles of the ABO blood group gene is well known The A allele and the B allele are both _____over the O allele.
Question 23
In humans a fruit flies, males are ________ for genes on the Y chromosome and are also considered the ________ sex
- hemizygous / homogametic
- hemizygous / heterogametic
- heterozygous / homogametic
- heterozygous / heterogametic
- hemizygous / homozygous
Question 24
______ epistasis can result in a dihybrid cross in which the F2 progeny have phenotypic ratios of 9:3:4.
Question 25
Griffith’s transformation experiments showed that ___________.
- DNA was the genetic material.
- DNA was comprised of A.T.G. and C
- RNA was the genetic material
- DNA was double helix
Question 31
Which of the following assumptions of the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium model are violated when allele frequencies fluctuate at random from one generation to the next?
- Random mating is occurring
- The population size is infinite
- No mutation is occurring
- No natural selection is occurring
Question 32
The EFFECTS of genetic drift are most pronounced In _________ populations.
- ginormous
- medium
- large
- small
Question 33
Genetic drift results in both _____ genetic diversity within populations, and ______ genetic divergence between populations.
- decreased / increased
- increased / increased
- decreased / decreased
- increased / decreased .
Question 34
You examine a population of seals and find that 100 males contribute gametes to the next generation, while 234 females contribute gametes to the next generation. What is the effective population size (to the nearest whole number)’
- 280
- 334
- 167
- 234
- 100
Question 35
What is the ultimate source of all genetic variability?
- mutation
- nonrandom mating
- natural selection
- genetic drift
- immigration
Question 36
The relative fitness of three genotypes A1A1A1A2 and A2A2 at the A-Gene are : w11=1, w12=0.5, w22 = 0.1, respectively. The population starts out in Handy Weinberg Equilibrium, and the frequency of the A1 allele at that starting time is 0.7. What is the allele frequency after one generation of selection?
- 0.3
- 0.09
- 0.69
- 0.49
- 0.7
- 1.0
- 0.01
- 0.84
- 0.16
- 0.0
- 0.48
- 0.3
Question 37
Which of the following are examples of postzygotic isolating barriers?
- hybrid inviability
- mechanical isolation
- behavioral isolation
- gamete competition
- hybrid sterility
- phenological isolation
Question 38
Dobzhansky and MuIIer’s verbal model described a plausible mechanism for the evolution of ________ isolation.
Question 39
Traits that show continuous (as opposed to categorical/discrete) variation are known as ________ traits.
Question 40
You plant 500 individuals, of a completely inbred line of Mimulus nasutus plants. You measure plant height in greenhouse conditions and note that the mean plant height is 5cm with a standard deviation of 2. The variation in plant height is due to:
- environmental differences among the plants
- epistatic interactions
- genotype x genotype interactions
- genetic differences among the plants
- genotype x environment interactions
Question 41
You plant 500 individuals, of a completely inbred line of Mimulus nasutus plants. You measure plant height in controlled greenhouse conditions and note that the mean plant height is 5cm with a standard deviation of 2. Around 95% of all M. nasutus plants measures in this study will fall between __________
- 4 and 6 cm
- 2 and 8 cm
- all plans will be 5 cm
- 1 and 9 cm
- 3 and 7 cm
Question 42
You cross completely inbred lines of M. nasutus (small plant) and M. guttotus (large plant) and find that height variation measured within each cross type is similar in parental and F1 (intermediate plant) generations. When you plant all of these crosses (parentals, F1 and F2 plants) in a common garden, you find an explosion of variation in the F2 plants (much wider distribution of plant heights relative to the other classes). This variation is likely due to:
- the fact that F2 plants are likely more adapted to common garden conditions.
- increased genetic variation in the F2.
- the fact that F1 plants are likely more adapted to common garden conditions
- increased environmental variation in the F2.
- the fact that both parental plants are likely more adapted to common garden conditions.
Question 43
If a DNA molecule contains 20% A, approximately what percentage of G will be present?
- 60%
- 30%
- 50%
- 20%
- 40%
Question 44
DNA replication is_________.
- semiliberal
- semidispersive
- semiconservative
- semimoderate
- moderate
- dispersive
- liberal
- conservative
Question 45
New DNA strands are manufactured in a _________ to direction.
- C’ to N’
- 5’ to 3’
- 3’ to 5’
- 3’ to 3’
- 5’ to 5’
- N’ to C’
Question 46
Which strand below would make the sequence 5’ AAACGCTT 3’ a double stranded DNA molecule?
- None of these are correct
- 5’ TTCGCAAA 3 ‘
- 5’ AAACGCTT 3’
- 5’ TTTGCGAA 3’
- 3’ TTTGCGAA 5’
Question 47
Okazaki fragments are produced from the _________ of parental DNA?
- leading strand
- semidispersive strand
- template strand
- dispersive strand
- lagging strand
- coding strand
- noncoding strand
Question 48
Which of the following do nonstructural genes code for?
- polypeptides
- snRNA
- proteins
- rRNA
- tRNA
Question
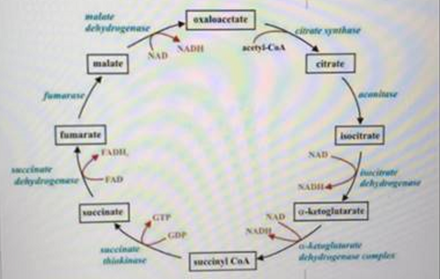
Use the above metabolic pathway to answer the following question.
You have an organism that Is a developmental mutant. In this organism, isocitrate builds up In its tissue. This is likely due to what enzyme being nonfunctional?
- isocitrate
- citrate
- GTP
- GDP
- isocitrate dehydrogenase
- NAD
- NADH
- aconitase
Question

Use the above metabolic pathway to answer the following question.
If succinate dehydrogenase is non-functional, which molecule will build up in the tissue of this organism?
- succinate
- GTP
- GDP
- Succinate thickinase
- succinate dehydrogenase
- fumarate
- FADH
- FAD
Question 51
The process by which RNA is manufactured from a DNA coding region Is called _____ .
- transcription
- translation
- replication
- trans-am
- ransversion
Question 52
The process by which a sequence of messenger RNA is converted into a polypeptide is called _______ .
trans-am
transversion
replication
transcription
translation
Question 53
Which type of transcriptional termination requires formation of a stem loop secondary structure?
polymerase dependent
ρ dependent
whoah-independent
polymerase independent
whoah-dependent
ρ independent
Question 54
A prokaryotic mRNA transcript:
must have a poly-A tail added to it before it is translated
must have introns removed before it is translated
must be transported out of the nucleus before it is translated
must have 5’ methylated cap added to it before it is translated
undergoes coupling of transcription and translation
must be further processed before it is translated
Question 55
The sequence of a template strand of DNA is 3’TATTC 5: What is the corresponding sequence of the mRNA strand?
I’ve been accused of this being a tricky question in the past
3’ GUUAU 5’
3’ GTTAT 5’
5’ UAUUG 3’
3’ TATTG 5’
5’ TATTG 3’
3’ UAUUG 5’
Question 56
The primary enzyme responsible for transcription is__________.
Lactase
Aminoacyl-transferase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
Ligase
Question 57
Which of the following post-transcription modifications of mRNA must occur in eukaryotes before translation commences?
addition of a poly-A tail at the 5’ end
methylation of the 5’end of the mRNA
methylation of the 3’end of the mRNA
spicing of introns
removal of exons
splicing of exons
removal of introns
addition of a poly-A tail at the 3’ end of the mRNA
Question 58
The sequential order in which amino acids occur in a protein chain is known as that protein’s _____ structure
primary
Question 59
Eukaryotic rRNA transcription repeat units contain_____ spacers that separate the many copies
external transcribed
introns
internal transcribed
internal nontranscribed
exons
external nontranscribed
Question 60
A point mutation that causes a coding sequence to be changed to stop codon Is known as a ____ mutation
nonsense
Question 61
In the lac operon, which of the following are translated into proteins?
Lac-Y
Lac-I
Lac-O
Lac-Z
Lac-A
Question 62
The most common form of regulation of gene expression in bacteria occurs at what level?
protein degradation control
translational control
nuclear transport control
transcriptional control
Question 63
Colon cancer results from _______ mutations
1
4
3
more than 4
2

