Navigation » List of Schools, Subjects, and Courses » Geog 001 – Physical Geography » Quizzes » Chapter 2 Quiz » Chapter 2 Quiz Sample Answers

Chapter 2 Quiz
1. Which of the following is essential in order for GPS to function?
Locations on land instead of the ocean
Highly accurate clocks
A nearby base station on Earth’s surface
A small, radar unit
A GIS unit in a receiver
2. Which of the following should contain a brief summary of the map’s content or purpose?
The area within the map’s boundaries
The scale
The data source
The title
The legend
3. Which of the following is NOT a form of remote sensing?
Measurement by thermometer
Aerial photography
Color infrared photography
Thermal infrared imaging
Radar
4 This figure shows a series of isolines portraying rainfall on the continent of Africa.
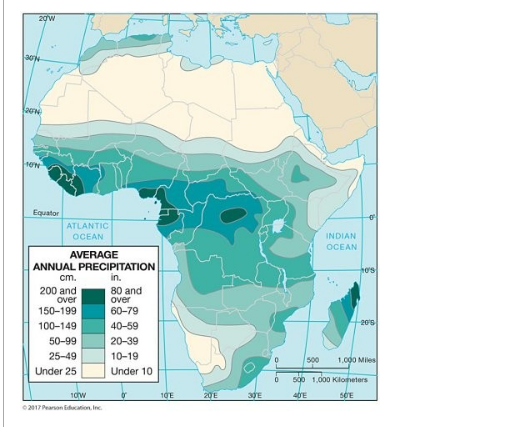
This figure is an isoline map of yearly rainfall over Africa. These specific type of isolines are ________.
isohyets
intervals
isotherms
elevation contours
isogonic lines
5. If one wished to produce a map that focused on the continents and showed little of the world’s oceans, then she/he should use a(n) ________ projection.
large-scale
equal-area
azimuthal
interrupted
conical
6. A(n) ________ scale remains correct even if the map is enlarged or reduced when reproduced.
large
isogonic
color
representative fraction
graphic
7. ________ is the major dilemma of mapmaking.
The inclusion of too much information on a map
Conformality versus scale
Conic versus azimuthal projections
Equivalence versus conformality
Scale versus equivalence
8. Map projections are mainly derived ________.
from interpolation
by analogy
mathematically
from aerial reconnaissance
by osmosis
9. The scale of “an inch on the map represents two miles on the surface of the Earth” would be CLOSEST to which representative fraction?
1:60,000
1:120,000
1:1,000,000
1:12
1:200,000
10. A disadvantage of globes compared to maps is that globes are NOT ________.
conformal
accurate
able to show as much detail
equivalent
suitable for use in class
11. “Scale” relates ________ to ________.
Earth distance, map distortion
map distortion, map distance
map distance, map distance
Earth distance, Earth distance
map distance, Earth distance
12. The property of equivalence portrays accurate size although it ________.
bends parallels
distorts shapes
stretches the circle of tangency
renders the poles as lines
13. The global positioning system (GPS) is based on ________.
large, expensive receivers
gravity waves from the Sun and Moon
aerial photography
data from satellites
infrared light sources
14. Conformal maps greatly distort ________ of continents in higher latitudes.
shapes
the latitude
the longitude
sizes
the number
15. Title, date, and legend are three ________.
components that are never all together on a map
map essentials
things that can be left off of a map
suggested map components
informative features usually appearing on the back of a map
16. Which of the following is most closely identified with multispectral remote sensing?
Microwave imaging
Color infrared photography
Landsat
Radar imaging
Thermal infrared scanning
Chapter 2 Quiz Answers
1. Which of the following is essential in order for GPS to function?
Locations on land instead of the ocean
Highly accurate clocks
A nearby base station on Earth’s surface
A small, radar unit
A GIS unit in a receiver
Answers Highly accurate clocks

